Leírás
Алтернатива на SolBan на Idelabs
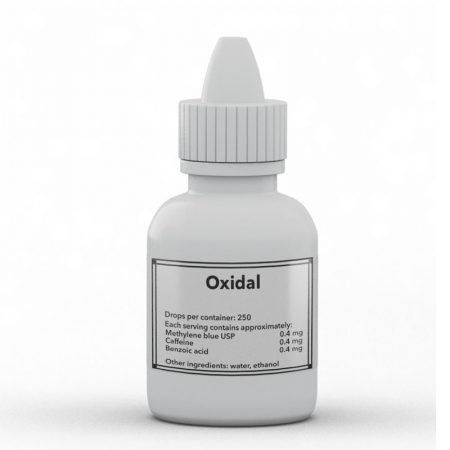
Представяме ви Solaris – иновативен дерматологичен спрей, създаден да осигури ефективна слънцезащита и да подпомогне здравето на кожата чрез синергичното действие на научно обосновани активни съставки.
Състав и механизъм на действие:
-
Ниацинамид (Витамин B3): Тази водоразтворима форма на витамин B3 притежава значителни противовъзпалителни и антиоксидантни свойства. Топичното приложение на ниацинамид подобрява бариерната функция на кожата, намалява трансепидермалната загуба на вода и регулира производството на себум. Клинични изследвания показват, че ниацинамидът може да намали хиперпигментацията и да подобри еластичността на кожата.
-
Кофеин: Този алкалоид с мощни антиоксидантни свойства инхибира фотокарциногенезата чрез абсорбция на ултравиолетовите лъчи и намаляване на образуването на реактивни кислородни видове. Топичното приложение на кофеин е свързано с намаляване на еритема, индуцирана от UVB лъчение, и предпазване от фотостареене.
-
Ацетилсалицилова киселина (Аспирин): Като нестероидно противовъзпалително средство, аспиринът инхибира циклооксигеназните ензими, намалявайки производството на простагландини, които медиират възпалителни реакции. Топичното приложение на аспирин може да намали кожното възпаление и да предпази от UV-индуцирани увреждания.
-
Сукцинова киселина: Този компонент е известен със способността си да повишава нивата на аденозинтрифосфат (ATP) в клетките, което е от съществено значение за енергийния метаболизъм и регенерацията на кожата. Повишените нива на ATP подпомагат растежа на косата и подобряват общото състояние на кожата.
Начин на употреба и препоръки:
-
Нанасяне: Разклатете добре преди употреба. Нанесете равномерен слой от Solaris върху чиста и суха кожа, като се фокусирате върху зоните, изложени на слънце. Избягвайте контакт с очите и лигавиците.
-
Честота на приложение: За оптимална защита, нанасяйте продукта 15-20 минути преди излагане на слънце. Повтаряйте нанасянето на всеки два часа, особено след плуване, изпотяване или подсушаване с кърпа.
-
Допълнителни препоръки: Въпреки че Solaris осигурява ефективна защита, препоръчително е да избягвате прекомерното излагане на слънце между 10:00 и 16:00 часа, когато UV лъчението е най-силно. Носете защитно облекло, шапки и слънчеви очила като допълнителни мерки за предпазване.
Предимства на Solaris пред конвенционалните слънцезащитни продукти:
Много от традиционните слънцезащитни продукти съдържат химични UV филтри, които могат да действат като ендокринни разрушители, нарушавайки хормоналния баланс на организма. Тези вещества могат да проникнат през кожата и да имат потенциално вредни ефекти върху здравето.
За разлика от тях, Solaris използва комбинация от активни съставки като ниацинамид, кофеин, ацетилсалицилова киселина и сукцинова киселина, които не само осигуряват ефективна слънцезащита, но и подобряват общото състояние на кожата. Тази формула минимизира риска от нежелани реакции и предоставя безопасна алтернатива на конвенционалните продукти.
Избирайки Solaris, вие се доверявате на продукт, който съчетава научно доказани съставки с висока ефективност и безопасност, без компромис със здравето ви.
https://lowtoxinforum.com/threads/solban-liquid-aspirin-caffeine-niacinamide-mix.5830/
1. NIACINAMIDE
Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. – PubMed – NCBI
Topical niacinamide reduces yellowing, wrinkling, red blotchiness, and hyperpigmented spots in aging facial skin. – PubMed – NCBI
A review of nicotinamide: treatment of skin diseases and potential side effects. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide and the skin. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide – biologic actions of an emerging cosmetic ingredient. – PubMed – NCBI
1.1 Hyperpigmentation and Skin Aging (niacinamide)
Topical niacinamide reduces yellowing, wrinkling, red blotchiness, and hyperpigmented spots in aging facial skin. – PubMed – NCBI
A review of nicotinamide: treatment of skin diseases and potential side effects. – PubMed – NCBI
Niacinamide – mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. – PubMed – NCBI
Niacinamide: A B vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. – PubMed – NCBI
The clinical anti-aging effects of topical kinetin and niacinamide in Asians: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, split-face comparativ… – PubMed – NCBI
Topical niacinamide 4% and desonide 0.05% for treatment of axillary hyperpigmentation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. – PubMed – NCBI
Reduction in the appearance of facial hyperpigmentation after use of moisturizers with a combination of topical niacinamide and N-acetyl glucosamin… – PubMed – NCBI
Reduction in facial hyperpigmentation after treatment with a combination of topical niacinamide and tranexamic acid: a randomized, double-blind, ve… – PubMed – NCBI
A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. – PubMed – NCBI
The effect of 2% niacinamide on facial sebum production. – PubMed – NCBI
Moisturizing effects of topical nicotinamide on atopic dry skin. – PubMed – NCBI
1.2 UV Damage (niacinamide)
Nicotinamide-containing sunscreens for use in Australasian countries and cancer-provoking conditions. – PubMed – NCBI
Topical nicotinamide modulates cellular energy metabolism and provides broad-spectrum protection against ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppre… – PubMed – NCBI
Ultraviolet A radiation: its role in immunosuppression and carcinogenesis. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide enhances repair of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage in primary melanocytes. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide reduces photodynamic therapy-induced immunosuppression in humans. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide enhances repair of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage in human keratinocytes and ex vivo skin. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide downregulates gene expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and tumour necrosis factor-α gene … – PubMed – NCBI
Oral and systemic photoprotection. – PubMed – NCBI
Photoprotective effects of nicotinamide. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide prevents ultraviolet radiation-induced cellular energy loss. – PubMed – NCBI
Oral nicotinamide protects against ultraviolet radiation-induced immunosuppression in humans. – PubMed – NCBI
UV radiation-induced immunosuppression is greater in men and prevented by topical nicotinamide. – PubMed – NCBI
[The intervention of nicotinamide on skin melanocyte’s cell proliferation after UVA (365 nm) exposed.]. – PubMed – NCBI
Prevention of photoimmunosuppression and photocarcinogenesis by topical nicotinamide. – PubMed – NCBI
Effects of nicotinamide on mouse skin tumor development and its mode of action. – PubMed – NCBI
Nicotinamide and nicotinamide analogues as antitumor promoters in mouse skin. – PubMed – NCBI
2. CAFFEINE
Follicular penetration of topically applied caffeine via a shampoo formulation. – PubMed – NCBI
The role of hair follicles in the percutaneous absorption of caffeine. – PubMed – NCBI
Topical delivery of caffeine from some commercial formulations. – PubMed – NCBI
2.1 Sunscreen effects (caffeine)
Caffeine and caffeine sodium benzoate have a sunscreen effect, enhance UVB-induced apoptosis, and inhibit UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis in SKH-1 … – PubMed – NCBI
2.2 Skin cancer (caffeine)
Topical applications of caffeine or (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) inhibit carcinogenesis and selectively increase apoptosis in UVB-induced skin tumors in mice
A novel topical targeting system of caffeine microemulsion for inhibiting UVB-induced skin tumor: characterization, optimization, and evaluation. – PubMed – NCBI
Caffeine decreases phospho-Chk1 (Ser317) and increases mitotic cells with cyclin B1 and caspase 3 in tumors from UVB-treated mice. – PubMed – NCBI
Caffeine decreases phospho-Chk1 (Ser317) and increases mitotic cells with cyclin B1 and caspase 3 in tumors from UVB treated mice
Effect of caffeine on UVB-induced carcinogenesis, apoptosis, and the elimination of UVB-induced patches of p53 mutant epidermal cells in SKH-1 mice. – PubMed – NCBI
Protection from photodamage by topical application of caffeine after ultraviolet irradiation. – PubMed – NCBI
Inhibitory effects of tea and caffeine on UV-induced carcinogenesis: relationship to enhanced apoptosis and decreased tissue fat. – PubMed – NCBI
Stimulatory effect of topical application of caffeine on UVB-induced apoptosis in mouse skin. – PubMed – NCBI
2.3 Other skin conditions (caffeine)
The effect of topically applied aspirin on localized circumscribed neurodermatitis. – PubMed – NCBI
Topical treatment of cutaneous herpes simplex virus-1 infection in mice with a specially formulated caffeine gel (Cafon). – PubMed – NCBI
Effect of caffeine and testosterone on the proliferation of human hair follicles in vitro. – PubMed – NCBI
Histopathological evaluation of caffeine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in efficient treatment of cellulite. – PubMed – NCBI
Role of Caffeine in the Management of Androgenetic Alopecia
Pharmacokinetics for topically applied caffeine in the rat. – PubMed – NCBI
Effectiveness of topical caffeine in cataract prevention: studies with galactose cataract. – PubMed – NCBI
Evaluation of the efficacy of topical caffeine in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. – PubMed – NCBI
Caffeine inhibits paresthesia induced by herpes simplex virus through action on primary sensory neurons in rats. – PubMed – NCBI
3. ASPIRIN
Combined patch containing salicylic acid and nicotinamide: role of drug interaction. – PubMed – NCBI
Design of a transdermal delivery system for aspirin as an antithrombotic drug. – PubMed – NCBI
Transdermal modification of platelet function. A dermal aspirin preparation selectively inhibits platelet cyclooxygenase and preserves prostacyclin… – PubMed – NCBI
Topically applied aspirin decreases histamine-induced wheal and flare reactions in normal and SLS-inflamed skin, but does not decrease itch. A rand… – PubMed – NCBI
Topically applied aspirin rapidly decreases histamine-induced itch. – PubMed – NCBI









Értékelések
Még nincsenek értékelések.